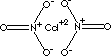| CADMIUM NITRATE TETRAHYDRATE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 10325-94-7 (parent), 10022-68-1 (tetrahydrate) |
|
| EINECS NO. | 233-710-6 (parent) | |
| FORMULA | Cd(NO3)2 · 4H2O | |
| MOL WT. | 308.48 | |
|
HS CODE |
2834.29.5100 | |
| TOXICITY | Oral Rat LD50: 300mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | Cadmium(II) nitrate tetrahydrate (1:2:4); C.I. 77192; | |
| Cadmium dinitrate tetrahydrate; Cadmium nitrate tetrahydrate; Dusicnan kademnaty; Nitric acid cadmium salt tetrahydrate; | ||
| SMILES | [N+](O)(=O)[O-].[N+](O)(=O)[O-].[Cd+2] | |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Cadmium Salt |
|
|
EXTRA NOTE |
Overall Carcinogenic Evaluation: Group 1 Poison/Deleterious Substance Code: 2S-22 A new nitrating agent for nuclear nitration of substituted |
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white crystal | |
| MELTING POINT |
59 C |
|
| BOILING POINT | 132 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 2.45 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | 2150 g/lo at 20 C | |
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY | Soluble in ammonia | |
| pH | 3.9 (50g/l) | |
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 4, Flammability: 0, Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Hygroscopic: absorbs moisture or water from the air. | |
|
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
||
|
http://www.inchem.org/ Local: Hazard Overview: Strong oxidizer. Contact with other material may cause a fire. Hygroscopic (absorbs moisture from the air). Causes eye and skin irritation. Harmful if swallowed, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin. Cancer hazard. Toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. Target Organs: Blood, skeletal structures, eyes, skin. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystal | |
| Cd(NO3)2 · 4H2O |
98.0% min |
|
|
CHLORIDES |
0.01% max |
|
| SULFATES |
0.05% max |
|
|
Fe |
0.01% max |
|
|
Pb |
0.05% max |
|
|
INSOLUBLES |
0.05% max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | ||
| HAZARD CLASS | 5.1 (Packing Group: II) | |
| UN NO. | 1477 | |
| SAFETY INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: T O N, Risk Phrases: 45-20/21/22-50/53-8, Safety Phrases: 53-17-36/37-45-60-61 | ||